Stutthof
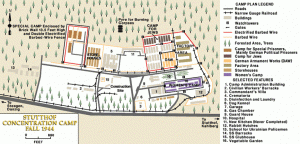 In September 1939, the Germans established the Stutthof camp in a wooded area west of Stutthof (Sztutowo), a town about 22 miles east of Danzig (Gdansk). The area was secluded: to the north was the Bay of Danzig, to the east the Vistula Bay, and to the west the Vistula River. The land was very wet, almost at sea level. The camp was situated along the Danzig-Elbing highway on the way to the popular Baltic Sea resort town of Krynica Morska.
In September 1939, the Germans established the Stutthof camp in a wooded area west of Stutthof (Sztutowo), a town about 22 miles east of Danzig (Gdansk). The area was secluded: to the north was the Bay of Danzig, to the east the Vistula Bay, and to the west the Vistula River. The land was very wet, almost at sea level. The camp was situated along the Danzig-Elbing highway on the way to the popular Baltic Sea resort town of Krynica Morska.
Originally, Stutthof was a civilian internment camp under the Danzig police chief. In November 1941, it became a "labor education" camp, administered by the German Security Police. Finally, in January 1942, Stutthof became a regular concentration camp.
Tens of thousands of people, perhaps as many as 100,000, were deported to the Stutthof camp. The prisoners were mainly non-Jewish Poles. There were also Polish Jews from Warsaw and Bialystok, and Jews from forced-labor camps in the occupied Baltic states, which the Germans evacuated in 1944 as Soviet forces approached.
 Conditions in the camp were brutal. Many prisoners died in typhus epidemics that swept the camp in the winter of 1942 and again in 1944. Those whom the SS guards judged too weak or sick to work were gassed in the camp's small gas chamber. Gassing with Zyklon B gas began in June 1944. Camp doctors also killed sick or injured prisoners in the infirmary with lethal injections. More than 60,000 people died in the camp.
Conditions in the camp were brutal. Many prisoners died in typhus epidemics that swept the camp in the winter of 1942 and again in 1944. Those whom the SS guards judged too weak or sick to work were gassed in the camp's small gas chamber. Gassing with Zyklon B gas began in June 1944. Camp doctors also killed sick or injured prisoners in the infirmary with lethal injections. More than 60,000 people died in the camp.
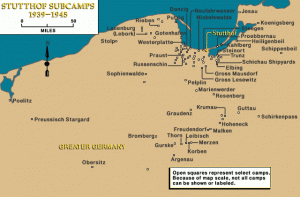
The Germans used Stutthof prisoners as forced laborers. Some prisoners worked in SS-owned businesses such as the German Equipment Works (DAW), located near the camp. Others labored in local brickyards, in private industrial enterprises, in agriculture, or in the camp's own workshops. In 1944, as forced labor by concentration camp prisoners became increasingly important in armaments production, a Focke-Wulff airplane factory was constructed at Stutthof. Eventually, the Stutthof camp system became a vast network of forced-labor camps; 105 Stutthof subcamps were established throughout northern and central Poland. The major subcamps were Thorn and Elbing.
The evacuation of prisoners from the Stutthof camp system in northern Poland began in January 1945. When the final evacuation began, there were nearly 50,000 prisoners, the overwhelming majority of them Jews, in the Stutthof camp system. About 5,000 prisoners from Stutthof subcamps were marched to the Baltic Sea coast, forced into the water, and machine gunned. The rest of the prisoners were marched in the direction of Lauenburg in eastern Germany. They were cut off by advancing Soviet forces. The Germans forced the surviving prisoners back to Stutthof. Marching in severe winter conditions and treated brutally by SS guards, thousands died during the march.
In late April 1945, the remaining prisoners were removed from Stutthof by sea, since Stutthof was completely encircled by Soviet forces. Again, hundreds of prisoners were forced into the sea and shot. Over 4,000 were sent by small boat to Germany, some to the Neuengamme concentration camp near Hamburg, and some to camps along the Baltic coast. Many drowned along the way. Shortly before the German surrender, some prisoners were transferred to Malmo, Sweden, and released to the care of that neutral country. It has been estimated that over 25,000 prisoners, one in two, died during the evacuation from Stutthof and its subcamps.
Soviet forces liberated Stutthof on May 9, 1945, and liberated about 100 prisoners who had managed to hide during the final evacuation of the camp.
From: Holocaust Encyclopedia

